G4-8
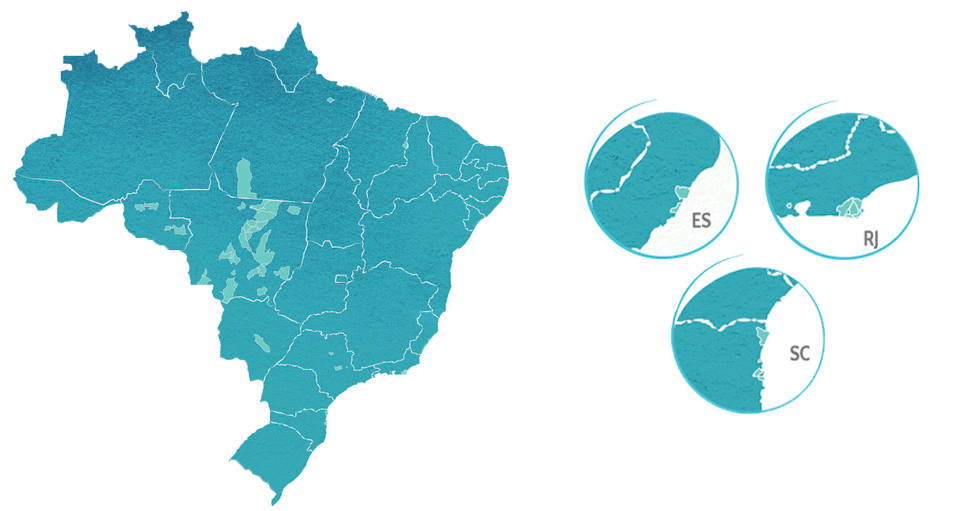
Aegea Saneamento e Participações S.A. is a Brazilian company headquartered in São Paulo (SP) that manages public water supply and collection and wastewater treatment concessions in 47 municipalities and nine states in Brazil. G4-3|G4-4|G4-5|G4-6|G4-7|G4-9
Created in 2010 by Grupo Equipav, the Company works autonomously and also relies on other capital partnerships, including with the International Finance Corporation (IFC), the Government of Singapore Investment Corporation (GIC) and the Global Infrastructure Fund (GIF).
In 2016, the year ended with revenue of R$992.4 million1 and 2,490 employees, in addition to expanding service to over 4,6 million people after gaining concessions in Ariquemes (RO), Bombinhas (SC), Serra (ES) and Vila Velha (ES). G4-9|G4-13
1. This amount does not include construction revenue – Brazilian Accounting Rules Committee (Comitê de Pronunciamentos Contábeis – CPC) 17.
Operations
G4-4|G4-6
| States |
Municipalities |
Operational units |
| Rio de Janeiro |
São João de Meriti |
Águas de Meriti |
| Armação dos Búzios |
Prolagos |
| Arraial do Cabo |
| Cabo Frio |
| Iguaba Grande |
| São Pedro da Almeida |
| Espírito |
Vila Velha* |
Vila Velha Ambiental |
| Serra* |
Serra Ambiental |
| São Paulo |
Piracicaba |
Águas do Mirante |
| Matão |
Águas de Matão |
| Holambra |
Águas de Holambra |
| Mato Grosso do Sul |
Campo Grande |
Águas Guariroba |
| Maranhão |
Timon |
Águas de Timon |
| Pará |
Barbacena |
Águas de São Francisco |
| Novo Progresso |
Nascentes do Xingu |
| Rondônia |
Ariquemes* |
| Buritis |
| Pimenta Bueno |
| Rolim de Moura |
| Mato Grosso |
Campo Verde |
| Carlinda |
| Cláudia |
| Jangada |
| Jauru |
| Marcelândia |
| Nortelândia |
| Pedra Preta |
| Peixoto de Azevedo |
| Poconé |
| Primavera do Leste |
| Santa Carmen |
| São José do Rio Claro |
| Sorriso |
| União do Sul |
| Vera |
| Porto Esperidião |
| Barra do Garças |
| Confresa |
| Guarantã do Norte |
| Matupá |
| Diamantino |
| Sinop |
| Paranatinga |
| Santa Catarina |
Bombinhas* |
Águas de Bombinhas |
| Penha |
Águas de Penha |
| Camboriú |
Águas de Camboriú |
| São Francisco do Sul |
Águas de São Francisco do Sul |
* Concessions gained in 2016.
Main indicators
| |
2016 |
2015 |
2014 |
2013 |
| Municipalities served |
47 |
43 |
35 |
29 |
| Population served (in millions) |
4.61 |
3.51 |
2.61 |
2.41 |
| Length of water system (in km) |
11,164 |
10,380 |
9,547 |
7,420 |
| Length of wastewater system (in km) |
4,676 |
4,266 |
4,178 |
3,589 |
| Water and wastewater savings (in thousands) |
|
|
|
|
| Water savings |
965.6 |
788.8 |
698.9 |
554.9 |
| Wastewater savings |
620.4 |
576.7 |
547.9 |
476.4 |
| Total |
1,486.0 |
1,365.5 |
1,246.8 |
1,031.3 |
| Billed water and wastewater volume (in millions of m3) |
|
|
| Billed water volume |
144.8 |
129.7 |
108.2 |
93.0 |
| Billed wastewater volume |
78.4 |
74.2 |
71.9 |
64.7 |
| Financial indicators |
|
|
|
|
| Rating – Fitch Rating |
Aegea “AA-” (bra);
Águas Guariroba “AA” (bra);
Prolagos “AA” (bra) |
Aegea “A+” (bra);
Águas Guariroba “AA-“ (bra);
Prolagos “AA-“ (bra) |
Aegea “A+” (bra);
Águas Guariroba “AA-” (bra);
Prolagos “AA-” (bra) |
Aegea “A+” (bra);
Águas Guariroba “AA-” (bra);
Prolagos “AA-” (bra) |
| Net operating revenue2 (R$ millions) |
992.4 |
795.1 |
599.5 |
491.7 |
| Ebitda (R$ millions) |
462.5 |
402.6 |
294.9 |
224.2 |
| Ebitda margin (%) |
46.6 |
50.6 |
49.2 |
45.6 |
1. If seasonality is considered for the municipalities served by Prolagos, the population served could reach 6.2 million.
2. Amounts do not include construction costs and revenue – CPC 17.
Management and governance
In 2016, after approval at the Shareholders’ Meeting of an increase in Aegea’s capital, the IFC and GIF were given a 5.49% and 4.80% stake in the Company, respectively, according to the following breakdown: G4-13

This new investment shows shareholder confidence in Aegea’s strategy and integrity. As a publicly traded company registered with Brazil’s Security and Exchange Commission (Comissão de Valores Mobiliários – CVM), the Company invests in the constant enhancement of organizational transparency and, since it was instituted, it has improved its corporate governance practices based on the principles of equality, accountability and corporate responsibility.
One important advance during the year was that the makeup of the Board of Directors was changed in the Articles of Organization, strengthening the presence of independent members (see “Governance structure”). The Integrity Management Group also started its work, reinforcing compliance measures that had already been adopted.
An increase in capital is proof of shareholder trust in the Company’s strategy and business model
Governance structure
G4-34
Shareholders’ Meeting
At the Shareholders’ Meeting, shareholders elect and dismiss members of the Board of Directors, analyze financial statements and decide on distribution of dividends, among other powers described in the Reference Form. Meetings are ordinarily held in the first four months after the end of each fiscal year and are held extraordinarily whenever necessary.
Board of Directors (BD)
Establishes management policies and guidelines and also elects and dismisses members of the Executive Board, the members of which it advises on executing strategic planning. During the fiscal year, the makeup was changed to at least three members and at most nine (with at least two independent members), all serving a re-electable one-year term. Board members meet ordinarily in the first month after the end of the fiscal year and extraordinarily whenever required.
Committees
According to statutory provisions, the Board of Directors is advised by four committees when dealing with strategic themes. These committees have three to five members, appointed by the BD to one-year, renewable terms.
Audit, Risks and Finance Committee
Provides information on risks and opportunities for projects and investments under study.

Project Assessment Committee
Advices on operational strategies based on studies of regulatory topics that may impact the Company’s performance.
Personnel Management Committee
Ensures the quality of financial information, internal controls and audits.
Regulation Committee
Assesses employee career plans, job policies and salaries.
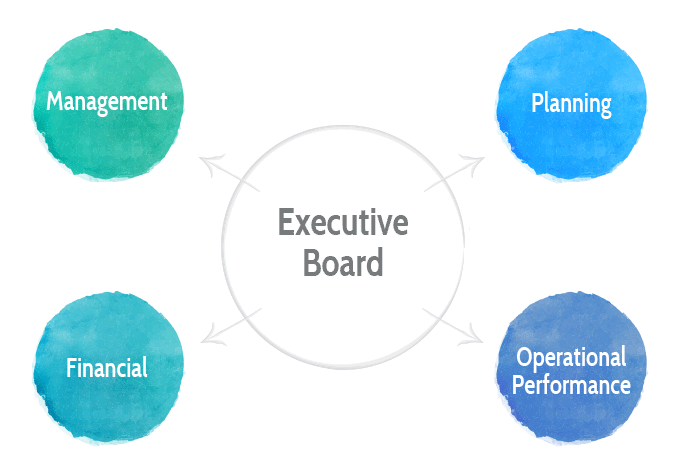
Executive Board
Strives to correctly manage the business, in line with the strategic planning and guidance of the Board of Directors. The Executive Board is made up of a minimum of three members and a maximum of seven members, with a CEO, CFO and Director of Investor Relations along with other directors with no specific designation. Directors serve one-year, renewable terms.
Integrity management
G4-DMA Child labor|G4-DMA Forced or compulsory labor|G4-DMA Indigenous rights|G4-DMA Anti-corruption|G4-DMA Social compliance|G4-DMA Assessment|G4-DMA Supplier human rights assessment|G4-56|G4-SO4
Aegea’s operations are based on the guidelines of its Code of Ethics, through which rules of conduct are shared for responsible business management. This document is based on the principles of respect for human rights and establishes criteria for relations with employees, suppliers, users, shareholders, the government and competitors.
In line with Brazilian laws, the Company does not donate to political parties or individual politicians (Law No. 9,504/97). Moreover, there were no cases of unfair competition or fines and non-monetary sanctions applied as a result of non-compliance with laws and regulations during the period covered by this report. G4-DMA Public policy|G4-DMA Anti-competitive behavior|G4-DMA Compliance|G4-SO6|G4-SO7|G4-SO8
Employees may make anonymous reports of breaches of the Code of Ethics and of non-compliance with laws through the Ethics Channel; reports are sent to the appropriate authority for verification and resolution.
In addition, the internal public is notified
regarding procedures to combat corruption and related to aspects of human rights that are relevant to operations. During the year, 1,021 employees underwent 3,358 hours of training – which represents training for 39.79% of the staff on these themes. G4-DMA Investment|G4-HR2|G4-SO4
As a result of a seminar on compliance and integrity aimed at directors and executives from all business units, the Integrity Management Group was created, which was initially formed of four Aegea employees. In 2016, this team began working to spread ethical principles throughout the Company. It also relied on outside consulting from Compliance Total, which began to work as an independent member of the group. Work done in partnership is geared towards constant enhancement of compliance practices. Because of its relevance, the Group will be made into a department under the Company’s organizational structure next year.
Sustainability Policy
Fostering sustainable development is part of Aegea’s core business, which is providing services to improve the quality of life and health of the population, in accordance with legal, environmental and social requirements. Since 2014, this work has been oriented by the Sustainability Policy, which establishes strategic guidelines and organizational objectives.
Sustainability Policy Guidelines

Economic pillar
- Improvement of financial results
- Continued and sustainable enhancement of processes
- Constant search for innovative solutions that add value to the business

Environmental pillar
- Prevention of pollution and environmental damage, as a result of Aegea’s direct and indirect activities
- Continual search for energy efficiency
- Sustainable use of natural resources, minimizing losses across processes

Social pillar
- Prevention of injuries and illnesses to employees and those working on behalf of the Company
- Ethical and transparent conduct in relation to
stakeholders
- Human development of the community where the Company operates, including employees
The Executive Board periodically monitors the Company’s performance, supported by the following management structure, which aims to assure fulfillment of objectives:

Disclosure Policy
The Disclosure Policy establishes rules for publication of material acts or facts and to maintain confidentiality in the event that information has not yet been communicated to the market. This document supplements CVM Instruction No. 358 and details the duties of the Finances and Investor Relations (IR) Division, which is responsible for mediation between Aegea and shareholders.
Publications are made available on the IR website (www.aegea.com.br/ri). Shareholders can contact the team by phone (+55 11 3818-8150) or by e-mail (ri@aegea.com.br), in addition to participating in visits to operating units, quarterly phone conferences and events with directors to discuss results. G4-26
Risk management
G4-DMA Economic performance|G4-2|G4-14
Aegea maintains a risk matrix and monitors political, social and economic aspects in order to forecast scenarios that could impact results. This preventive attitude allows for appropriate adaptation of strategic planning and enhancement of internal processes for the Company’s longevity. Among the main risks are:
Interest rate risk | Market interest rates can cause the fair value of future cash to become unbalanced, which poses a risk to Aegea in terms of its long-term obligations. In this sense, the Company simulates refinancing and renewals of existing positions based on its main financial assets and liabilities so as to better calculate the impact on results.
Credit risk | Connected to the possibility of losses resulting from non-fulfillment of financial obligations agreed to with borrowers or contract counterparties. To mitigate this risk, Aegea conservatively manages its cash position and working capital.
Liquidity risk | The result of a lack of resources to fulfill obligations undertaken due to an imbalance between assets and liabilities, which could result in the need for early liquidation. The Company periodically revises the mechanisms that allow for funding to be raised in an effort to reverse positions that could be prejudicial to the liquidity of the Company and its controlled companies.
Macroeconomic risks | Rates of inflation, tax and monetary policies, political and economic instability, liquidity in the domestic market and government interventions in rates are some of the factors that could impact the Company’s financial results and operational performance. Although Aegea is unable to manage these occurrences, the Company looks at studies on the macroeconomic situation in Brazil in order to forecast scenarios to revise strategic planning and structure plans of action.
Default risk | Accounts due or not paid by users and government organizations can compromise the Company’s revenue stream. In 2016, Aegea reinforced efforts in oversight and debt negotiation programs to control the default rate, which was reduced by 1.2% in 2016 compared to the previous year (see “Financial capital”).
Risks related to climate factors | Periods of drought or substantial rainfall can cause decreases in revenue to fall and increases in costs and judicial actions, which harms the Company’s reputation. In the former scenario, less water flow from springs and reservoirs can interrupt the population’s supply and require costs for use of alternative sources until service is reestablished. While when floods result from heavy rainfall, they can paralyze supply and demand expenditures to adapt the water treatment process. G4-EC2
Pollution risk | Although the water supplied to users complies with the potability standards required by federal and state laws, the Company is subject to risks of contamination from supply sources as a result of third-party actions, such as dumping of chemical products in springs and the use of agricultural chemicals. There is also a risk of pollution from Wastewater Treatment Station (WWTS) overflow. The occurrence of these factors can change water quality and require the use of additional treatment materials, in addition to causing damage to biodiversity and Aegea’s image. To mitigate this risk, investments are made in expanding the wastewater network and to combat clandestine sewers.
Aegea forecasts scenarios is a structured manner to adapt its strategic planning and enhance internal processes
 More detailed information on risk factors is available at the Reference Form, available at www.aegea.com.br/ri.
More detailed information on risk factors is available at the Reference Form, available at www.aegea.com.br/ri.
Stakeholder engagement
G4-24|G4-25|G4-26
In 2016, the Company carried out internal work to update the map of stakeholders. Publics were identified based on a review of objectives, approaches and frequency of relations – as described below:
| Group |
Objective |
Approach and frequency |
| Users and communities |
Show the importance of services provided, as well as the benefits to public health and well-being. The goal is also to answer questions and be transparent in relation to operational processes. |
Constant relations through informational and institutional materials, educational initiatives and service at sales locations, by phone or over the internet. |
| Employees |
Retain and develop talent at the Company and its controlled companies. The goal is also to share values for alignment of conduct in striving for common results and objectives. |
Constant relations, aligned with the determinations of the Code of Ethics. |
| Suppliers |
Aimed at this public's compliance with the Company's standards of integrity. |
Constant relations, through targeted informational communications and shared values in the Company's Code of Ethics. |
| Investors and financial institutions |
Communicate financial and operational results achieved transparently and in accordance with the principles of corporate governance that govern Aegea's management. Relations are aimed at gaining this public's trust and generating capital to sustain the Company's growth. |
Constant relations, through the Investor Relations website and, periodically, through disclosures of material facts and quarterly and annual results, in addition to events and phone conferences. |
| Concession authority |
Provide accountability on contractual frameworks to governments in the locations where Aegea operates in order to gain this public's satisfaction. |
Work meetings scheduled during the year. |
| Government decision-makers |
Show Aegea's competency and operational efficiency, positioning the Company as a specialist in the segment in which it operates. |
Market events, according to the industry agenda. |
| Trade associations |
Guarantee collaboration and Aegea's leading role in developing the sector. |
The Company is an active participant in trade associations in order to deal with regulatory and industry matters. |
| Press |
Guarantee that the correct position is reported in relation to the Company. Aegea understands that this public spreads information and conveys the Company's credibility to the public. |
Constant relations. |
| Universities |
Strengthen the segment through development of professionals and communication of information related to academic research. |
Contests for universities to develop projects and other relationship actions periodically carried out. |
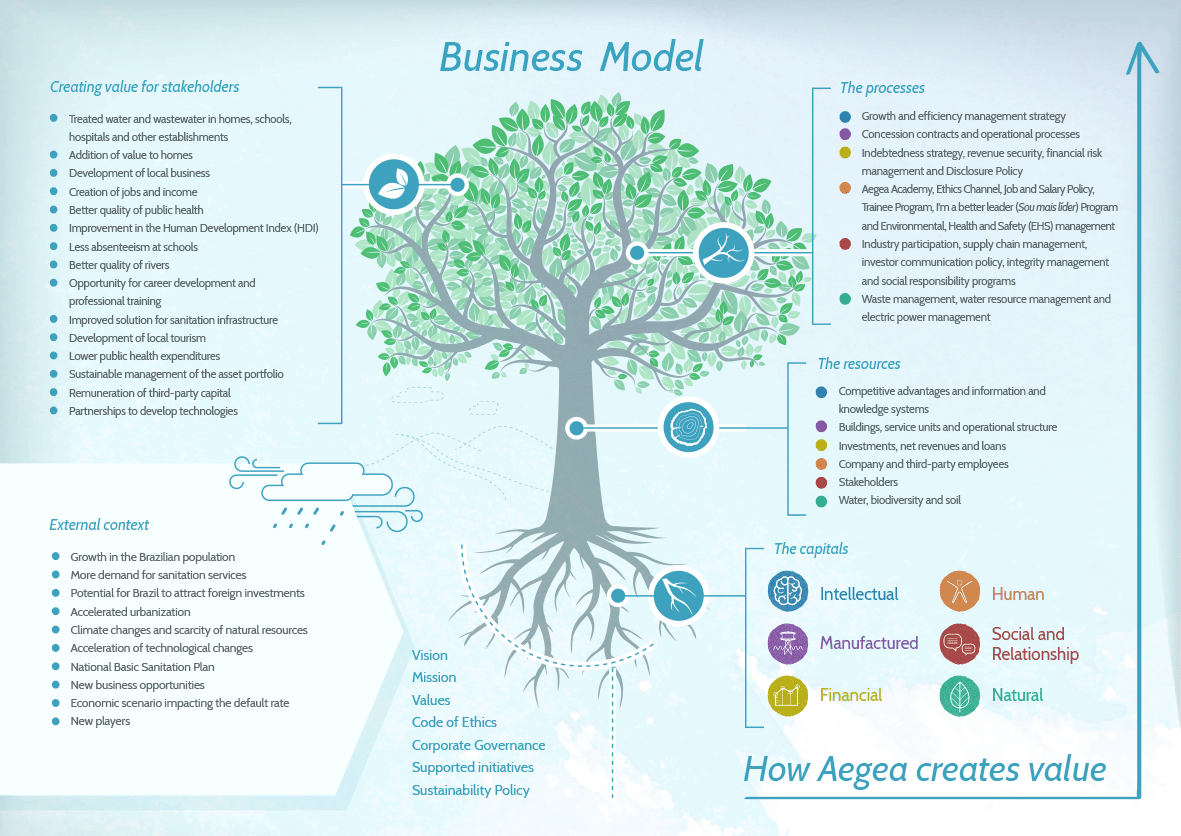
Business model
In an effort to advance application of International Integrated Reporting Council (IIRC) principles, the consulting firm responsible for this report advised Aegea on representation of its business model, which covers six types of capital – intellectual; manufactured; financial; human; social and relationship; and natural – as well as on the resources and processes through which the Company manages its business and relationships, in addition to the risks to which it is exposed and the opportunities arising therefrom. The aim is to show how Aegea creates and shares value with each stakeholder category.
In addition to qualitative interviews with the Executive Board, a work group was established with an internal team and members of the consulting firm in order to analyze the institutional policies, guidelines and documents which serve as the basis for development of the business model. The external context was also taken into account and, to do this, Company studies were considered to structure the SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats) and PwC Megatrends2. The following business model design was therefore created:
The tree – the inspiration for the creative concept of this publication – represents the Company’s development, growing in both the strength of its trunk (resources and internal processes) as well as the span of its canopy (values shared with stakeholders). The structure is supported by strong roots, which are nourished by the fundamental elements that permeate the entire organism.
2. Available at https://www.pwc.com.br/pt/publicacoes/institucionais/assets/2015/megatendencias_15.pdf.